
In Microsoft Excel, you often find numbers stored as text. This usually happens with imported or copy-pasted data. These text-based numbers seem like real numbers, but they act differently. Formulas don’t calculate correctly. Sorting fails to work, and your reports can show wrong results. That’s where learning how to convert text to number in Excel becomes essential.
What is “Text to Number” in Excel?
In Excel, “Text to Number” means turning cells that look like numbers into actual numbers. This is crucial for proper calculations, sorting, filtering, and data validation.
Key Indicators That a Number is Stored as Text:
- The number is left-aligned (default alignment for text).
- There’s a small green triangle in the top-left corner of the cell.
- Formulas like =SUM() or =AVERAGE() return incorrect results.
- Sorting doesn’t work as expected.
How to Convert Text to Number in Excel
You can convert text to numbers in several ways. Each method works best for specific situations. Let’s explore the most effective methods.
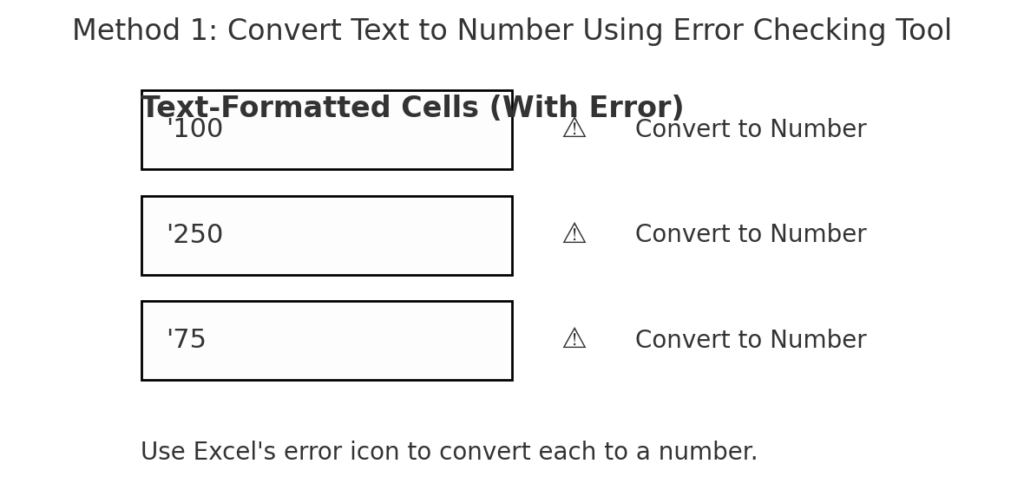
Method 1: Using the Error Checking Tool
Excel often identifies text-numbers and flags them.
Steps:
- Select the cell(s) with the green triangle error.
- Click on the warning icon ⚠️ that appears.
- Choose Convert to Number.
This instantly converts the selected cell(s) into a proper numeric format.
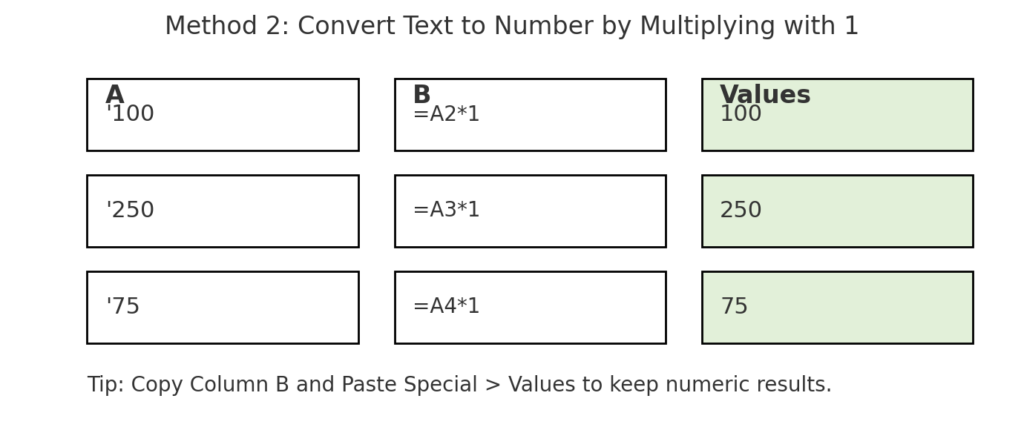
Method 2: Multiply by 1
This method uses a simple formula trick to force Excel to treat text as numbers.
Steps:
- In an empty column, enter:
=A2*1
- Press Enter and drag down.
- Copy and paste the result as values using Paste Special > Values.
This converts the text to a number using mathematical coercion.
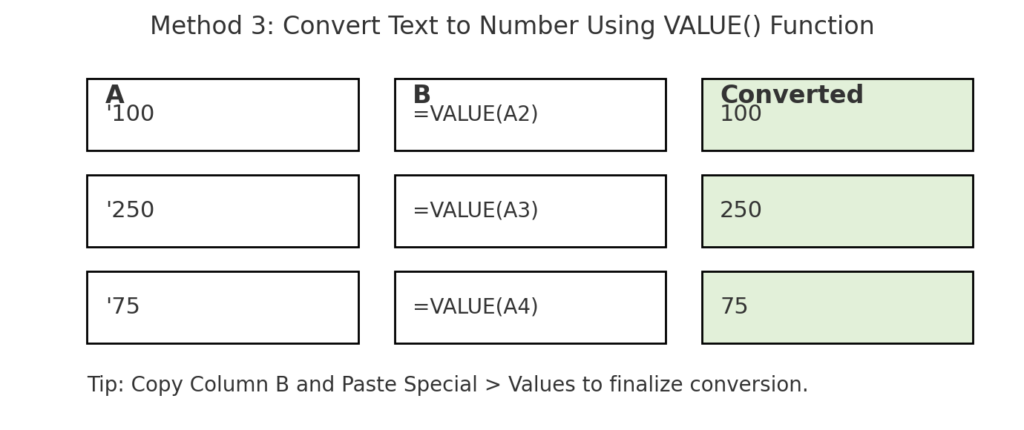
Method 3: Use =VALUE() Function
The VALUE function is designed specifically to convert text to numbers.
Syntax:
=VALUE(A2)
- Works best when your cells contain numeric values stored as text.
- Drag the formula down and paste the results as values.
Method 4: Text to Columns Wizard
A built-in tool that can also fix number formatting.
Steps:
- Select the column containing text-numbers.
- Go to Data > Text to Columns.
- In the wizard, click Next > Next > Finish.
This method makes Excel change the data into numbers, even if you don’t split the columns.

Method 5: Paste Special (Add Zero)
Another quick trick is to add 0 using Paste Special.
Steps:
- Type 0 in an empty cell and copy it.
- Select the text-based numbers.
- Right-click > Paste Special > Add > Click OK.
Excel will add 0 to each value, converting them to real numbers.
Method 6: Change Cell Format and Re-enter
Sometimes simply retyping can fix the format.
Steps:
- Select the cells > Right-click > Format Cells.
- Choose Number or General.
- Click OK.
- Press F2 in each cell and hit Enter to refresh.
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Importing Sales Data from CSV
ProductRevenueA”1200″B”1500″C”1800″
Revenue is stored as text (quotes indicate text). Using =VALUE(B2), you can convert and apply =SUM(B2:B4) accurately.
Example 2: Pasted Web Data
Copy-pasted numeric data from a website may appear like this:
Views1,0002,500
These will be treated as text. Use Text to Columns or =SUBSTITUTE(A2, “,”, “”)*1 to convert properly.
Example 3: Errors in Formulas
If you try to add cells and get wrong totals, one of the values might be text. For example:
=SUM(A2:A6)
Returns 0 if A2:A6 contain text-numbers. Use Convert to Number or =VALUE() to correct.
Benefits of Converting Text to Number in Excel
Accurate Calculations
Formulas like SUM(), AVERAGE(), and IF() require numeric values to function correctly.
Use Case: Financial summaries that depend on accurate total and average values.
Reliable Data Sorting and Filtering
Sorting text-based numbers can result in incorrect order (e.g., “100” comes before “20”). Converting to numbers ensures logical numeric sorting.
Use Case: Sales dashboards and reports.
Cleaner Visual Presentation
Numbers that are aligned to the right look neat and professional in reports and dashboards.
Use Case: Client-facing Excel reports.
Prevents Data Errors in Charts
Charts created from text-numbers may display incorrect visuals or ignore some data entirely. Numeric conversion fixes that.
Use Case: Visualizing monthly KPIs or revenue trends.
Enables Data Validation and Lookups
Functions like VLOOKUP(), XLOOKUP(), and MATCH() can fail. This happens when one column has text-based numbers, but the lookup value is a real number.
Use Case: Searching customer IDs or order totals.
Excel How To Convert Text to Number
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Why is Excel storing numbers as text?
Common reasons include:
- Importing data from CSV or the web
- Using apostrophes (like ‘1000)
- Manual typing, which can cause formatting problems.
How can I quickly check if a cell is a number or text?
Use the =ISTEXT(A2) or =ISNUMBER(A2) function to verify.
Will converting text to number change my data?
No — it only changes the data type, not the visible value (unless text is improperly formatted).
Can I convert multiple columns at once?
Yes. Select the full range. Then, use methods like Text to Columns, Paste Special, or array formulas.
How can I prevent numbers from being stored as text in future?
Always format columns as Number or General before entering or pasting data.
Conclusion
Turning text into numbers in Excel is a key skill. It helps keep data accurate, ensures correct calculations, and supports professional formatting. Excel offers simple tools for tasks like managing financial reports, processing sales figures, and cleaning imported data. You can use the VALUE function, Paste Special tricks, and the Text to Columns wizard. Using these methods helps you avoid formula errors, wrong sorting, and bad visualizations. This way, your spreadsheets stay functional and look great.
