
Microsoft Excel is a top tool for data analysis and reporting. It helps users organize, analyze, and present data effectively. Managing large datasets can cause problems like duplicate values. These duplicates can skew results, create calculation errors, and harm data integrity. To remove duplicates in Excel, you need to know a few key steps. It’s important for anyone who works with data often. In this guide, we’ll cover what duplicates are. We’ll also show you how to remove them with different methods. You’ll find examples and learn the long-term benefits of keeping your data clean.
What is a Duplicate?
A duplicate in Excel is when a data entry appears more than once. This can happen in one column or across several columns. These entries are the same. They often come from several sources, mistakes by users, or system bugs. Duplicates can lead to redundancy, misinterpretation of data trends, and incorrect summary results.
For example, if you track orders, you might see “John Smith” listed several times with the same order number. Excel could count this as multiple transactions. This can inflate your sales figures.
How to Eliminate Duplicates in Excel?
There are several ways to find and remove duplicates in Excel. Here are the most effective and commonly used methods:
Using the Built-in “Remove Duplicates” Feature
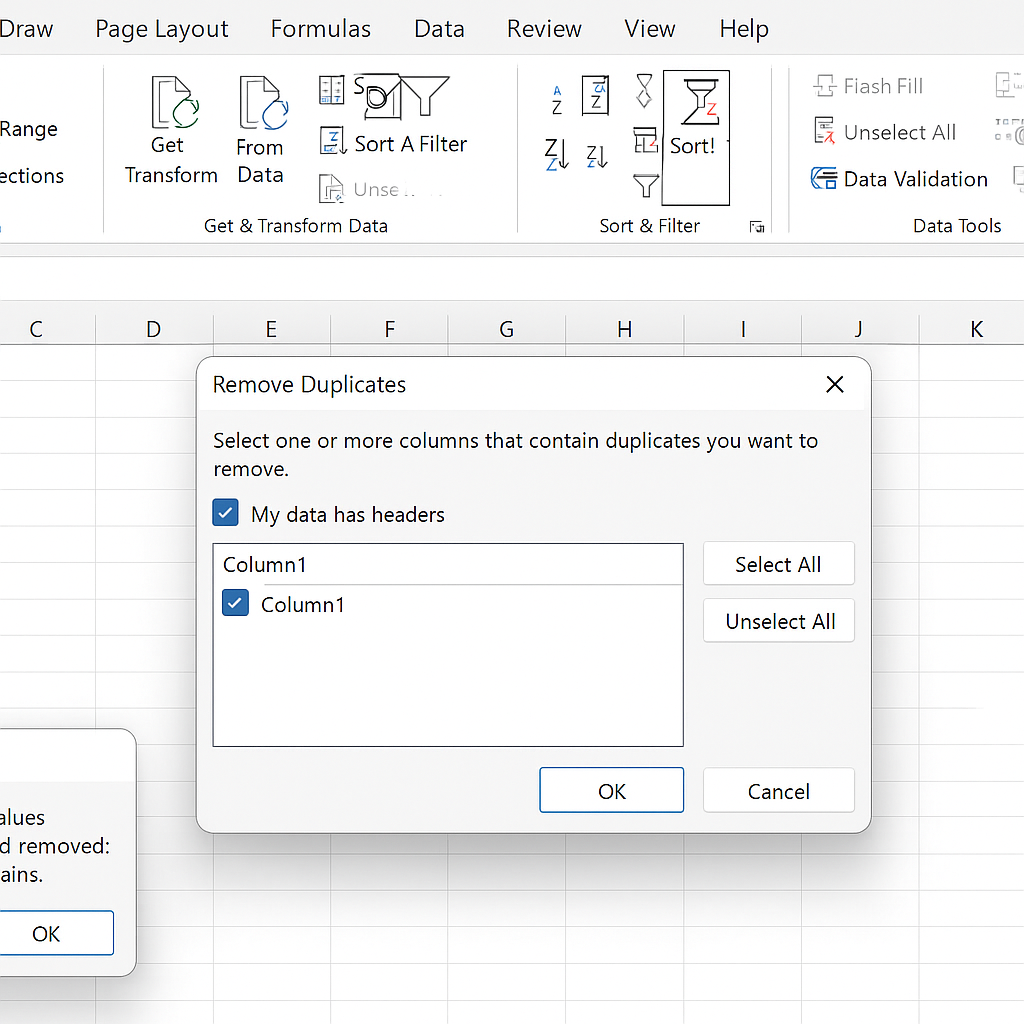
Excel provides a built-in feature to remove duplicate entries quickly:
- Select the range of cells or click inside the data table.
- Go to the Data tab on the Ribbon.
- Click on Remove Duplicates.
- A dialog box will appear allowing you to select one or more columns to check for duplicates.
- Click OK.
Excel removes duplicate rows. It shows a summary of duplicates removed and the count of unique values left.
Conditional Formatting to Highlight Duplicates
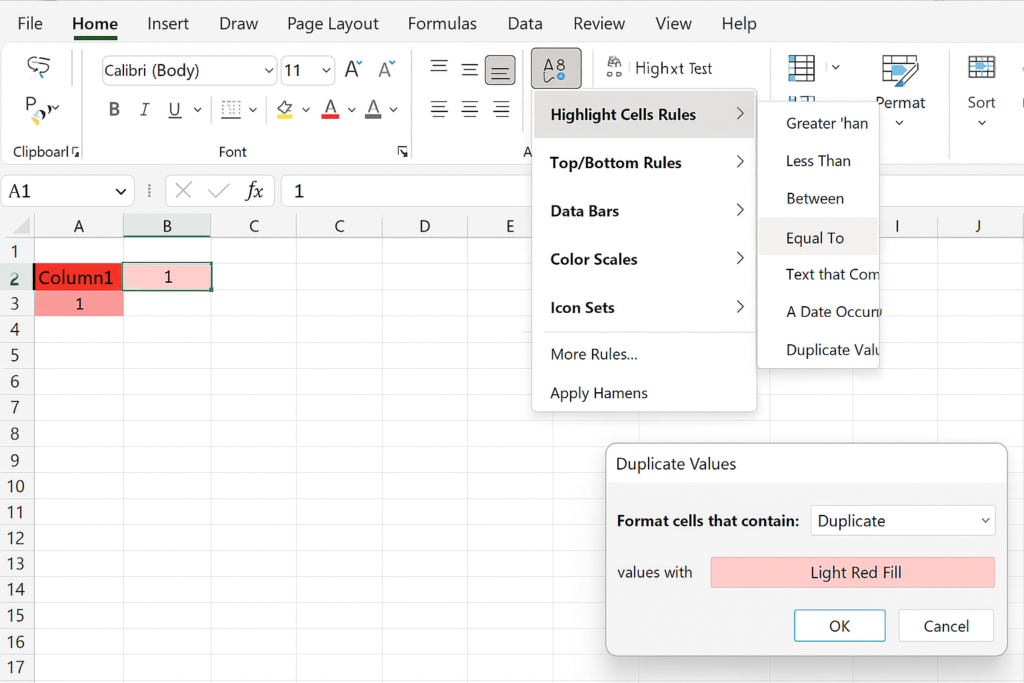
This method doesn’t remove duplicates but helps you spot them visually:
- Select the data range.
- Go to the Home tab.
- Click on Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cells Rules > Duplicate Values.
- Choose formatting options (e.g., red fill).
This is especially helpful for reviewing data before deciding to delete duplicates.
Using Advanced Filters
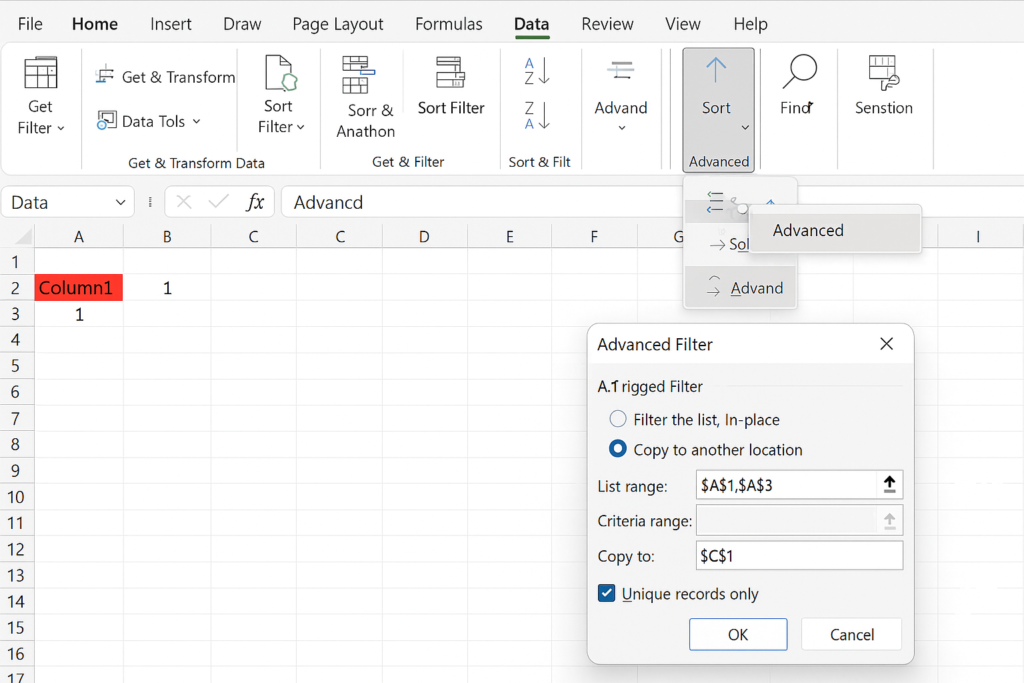
You can use Excel’s Advanced Filter to display only unique records:
- Select your data range.
- Go to the Data tab > Advanced.
- Choose “Copy to another location.”
- Check “Unique records only.”
- Define where to paste the filtered data.
This method helps you keep the original dataset and make a cleaned version.
Using Excel Formulas
You can use Excel functions to identify or count duplicates:
- COUNTIF Function: To mark duplicates
=IF(COUNTIF(A:A, A2)>1, “Duplicate”, “Unique”)
- IF + COUNTIFS: For more complex conditions across multiple columns
=IF(COUNTIFS(A:A, A2, B:B, B2)>1, “Duplicate”, “Unique”)
You can then filter by “Duplicate” and delete the rows manually or automate with macros.
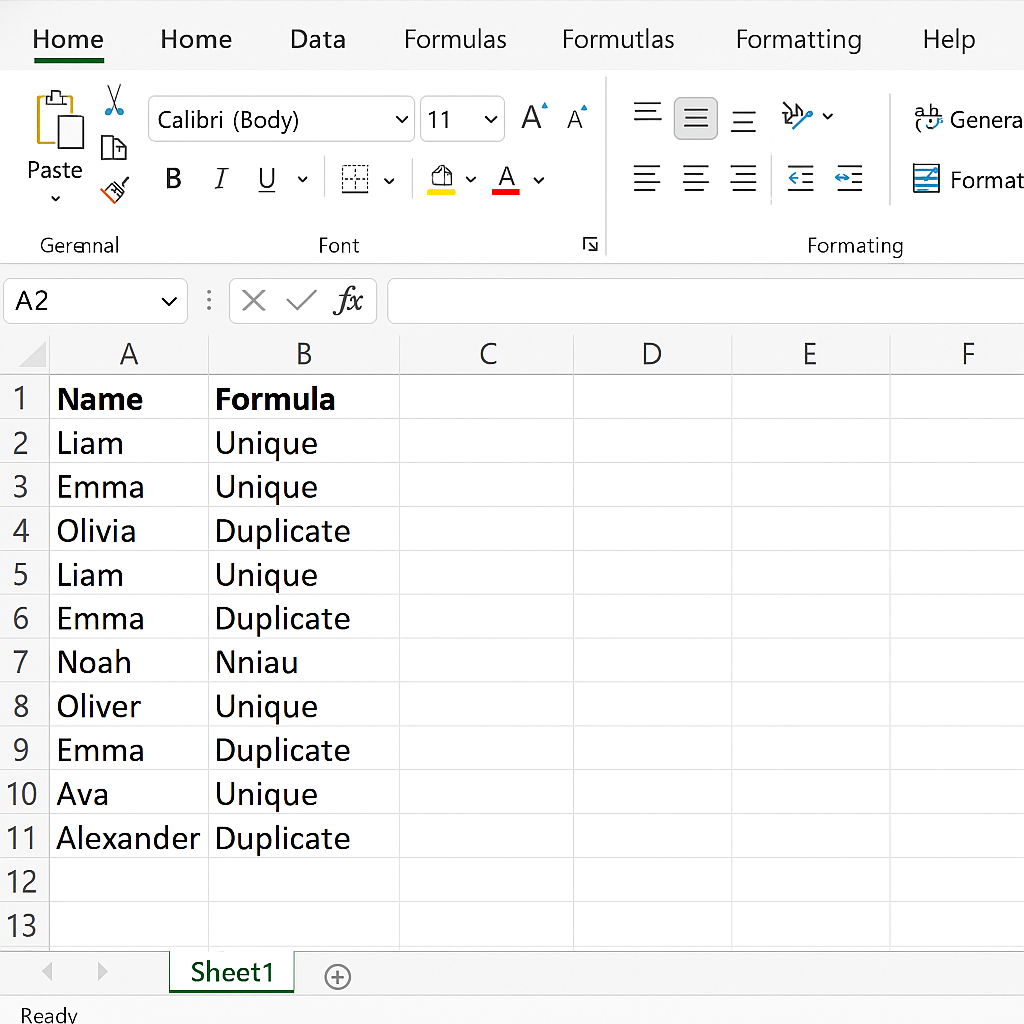
Examples
Example 1:
Removing Customer Duplicates Let’s say you have a customer list with the columns: Name, Email, Phone. If “John Doe” shows up twice with the same email and phone number, you can use “Remove Duplicates” for all three columns.
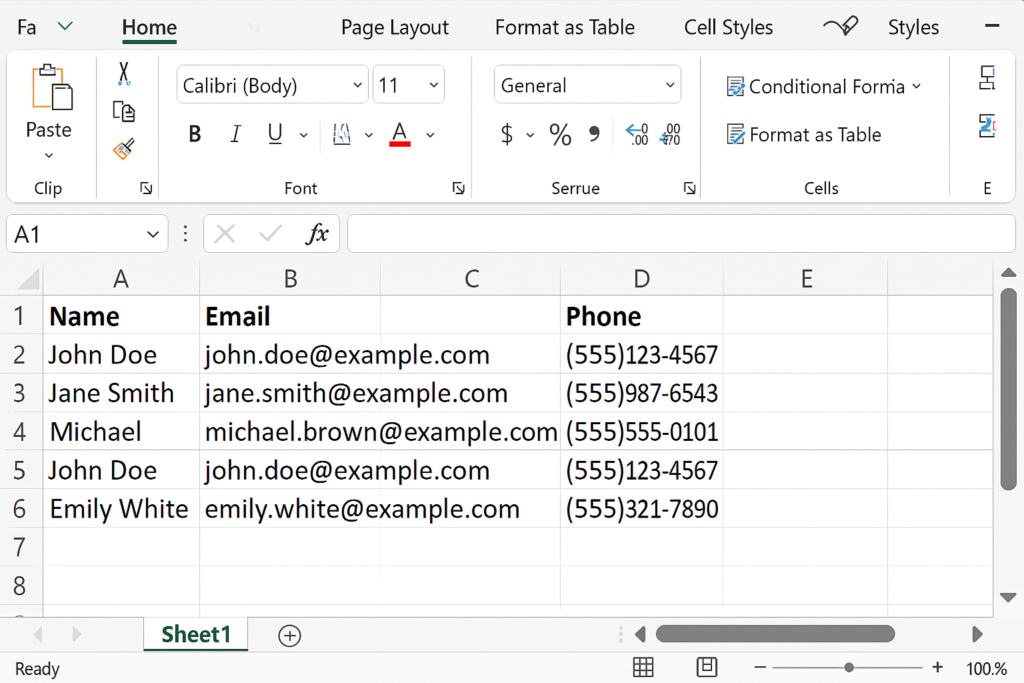
Example 2:
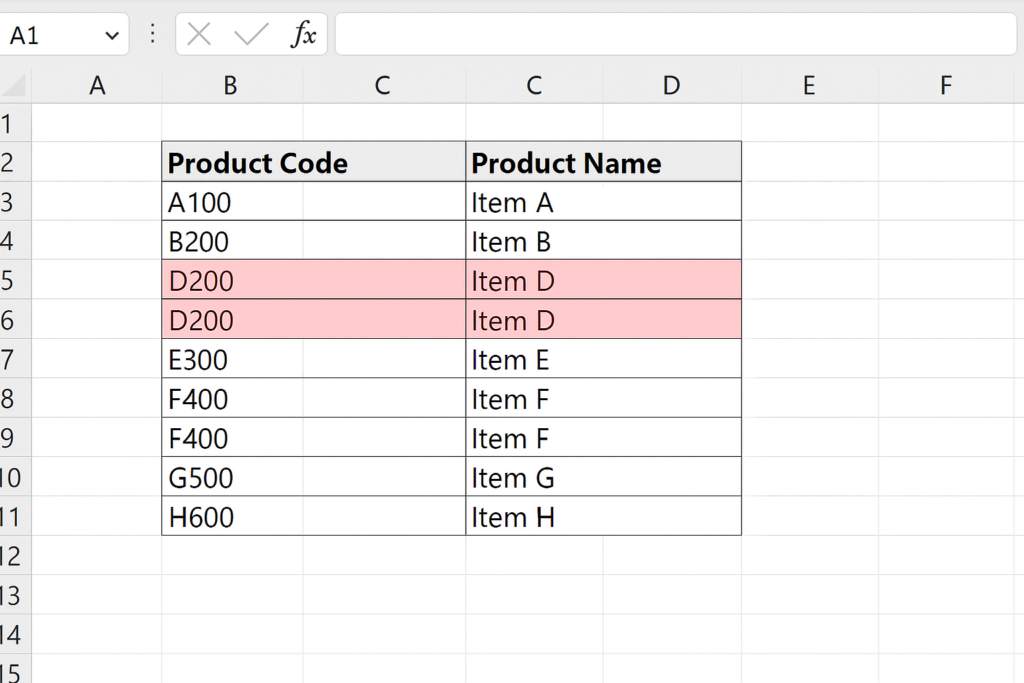
Highlighting Duplicate Product Codes A product inventory list contains product codes. Use Conditional Formatting to highlight any duplicate codes. Then manually verify which records to keep or delete.
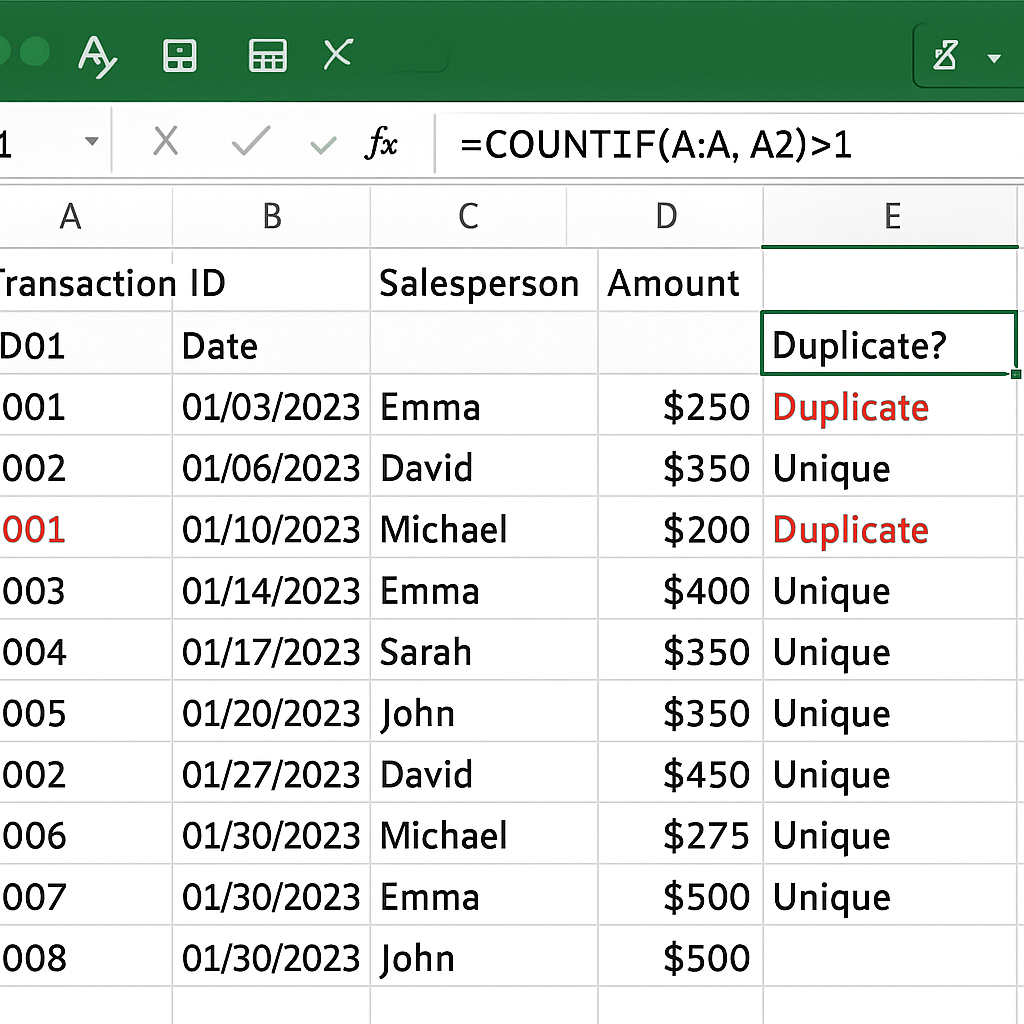
Example 3:
Using COUNTIF for Sales Records You’re managing monthly sales and want to identify if the same transaction ID appears more than once. Using COUNTIF can quickly flag those entries.
Benefits of Eliminating Duplicates
- Improved Data Accuracy: Duplicate entries can distort calculations like totals, averages, and percentages. Removing duplicates helps every data point play its part in your analysis. This leads to better insights and improved decision-making.
- Better System Performance: Especially in large Excel files, duplicate records can increase file size unnecessarily. Removing them can improve load times, reduce lag, and make formulas execute faster.
- Enhanced Data Integrity and Trust: Clean, duplicate-free data builds your credibility and professionalism when you work in teams or share spreadsheets with clients. Stakeholders can trust the insights derived from the dataset.
- Simplified Data Integration: When you import data into databases, CRMs, or cloud apps, duplicates can cause errors or conflicts. Clean data ensures seamless integration and avoids duplicates across systems.
- Compliance and Auditing: Many industries require data accuracy for compliance. Duplicate entries can be flagged during audits. Clean data helps meet regulatory standards more easily.
How to Remove Duplicates in Excel
FAQ’s
What happens if I accidentally remove unique values while removing duplicates?
Excel’s “Remove Duplicates” feature permanently deletes duplicates from the selected range. If you remove unique values by mistake, you can’t recover them automatically. You need a backup or to press Ctrl+Z right away to undo. It’s best to copy the data first or use filters before deleting anything.
Can I remove duplicates based on one column but keep the rest of the row data?
Yes, Excel allows you to choose which columns to check for duplicates. When you pick just one column, Excel deletes rows with repeated values in that column. However, it keeps the other data from the first row where the value appears.
Is there a way to prevent duplicate entries in Excel while entering data?
Yes, you can use Data Validation. Select the cells where data will be entered, go to Data > Data Validation > Custom, and enter a formula like:
=COUNTIF($A$1:$A$100,A1)=1
This prevents users from entering values that already exist in the range.
Can Power Query help in removing duplicates?
Absolutely. Power Query is a powerful tool in Excel to load, transform, and clean data. In Power Query Editor, you can use the “Remove Duplicates” feature with just a few clicks. It’s great for big datasets or tasks you do often. You can refresh and apply the same steps automatically.
Conclusion
Removing duplicates in Excel is a key data cleaning skill. It helps keep your data accurate, reliable, and efficient. Excel has many ways to handle duplicate data. You can use built-in tools, formulas, conditional formatting, or Power Query. Always back up your data before making changes. Also, check your datasets regularly for inconsistencies. Master these techniques to streamline your work. You’ll also create more credible and professional data presentations.
