
Excel is a top tool for organizing, analyzing, and reporting data. Professionals in all industries use it. Working with large datasets can be messy. You often find empty rows scattered in your spreadsheets. Blank rows can disrupt formulas. They can also make data imports tricky and complicate navigation in your workbook. Deleting empty rows in Excel is a simple skill. It boosts data accuracy and makes your spreadsheet easier to read. Plus, it keeps your files neat and professional. This guide explains empty rows. You’ll learn how to remove them using different methods. We’ll share examples, real-life scenarios, and the benefits of cleaning your data. Also, we’ll answer common user questions.
What Are Empty Rows in Excel?
Empty rows in Excel have no data. This means no text, numbers, formulas, formatting, or values in any cell. These rows may appear due to:
- Data imports from other systems or file formats (CSV, XML, etc.)
- Manual deletion of cell contents without removing the row itself
- Errors in data entry
- Copy-pasting irregular content from external sources (like web tables)
While one or two empty rows might seem harmless, a large number of them can lead to significant issues:
- Incorrect totals or averages
- Misleading data insights
- Inefficient sorting, filtering, or printing
- Problems with macros, pivot tables, or data connections
Cleaning these up ensures your spreadsheets remain reliable and performance-optimized.
How Can I Delete Empty Rows in Excel
Excel provides several built-in methods to remove blank rows. The right method depends on your data’s structure. It also depends on whether you want a quick cleanup or a repeatable process.
Method 1: Use Go To Special (Best for Smaller Datasets)
This is a quick and visual way to remove all blank rows in Excel.
Steps:
- Select your entire dataset or worksheet.
- Press F5 or go to Home > Find & Select > Go To Special.
- In the dialog box, select Blanks and click OK.
- Excel will highlight all blank cells.
- On the Home tab, in the Cells group, click Delete > Delete Sheet Rows.
Note: This method works best when each blank row has entirely empty cells across all columns.
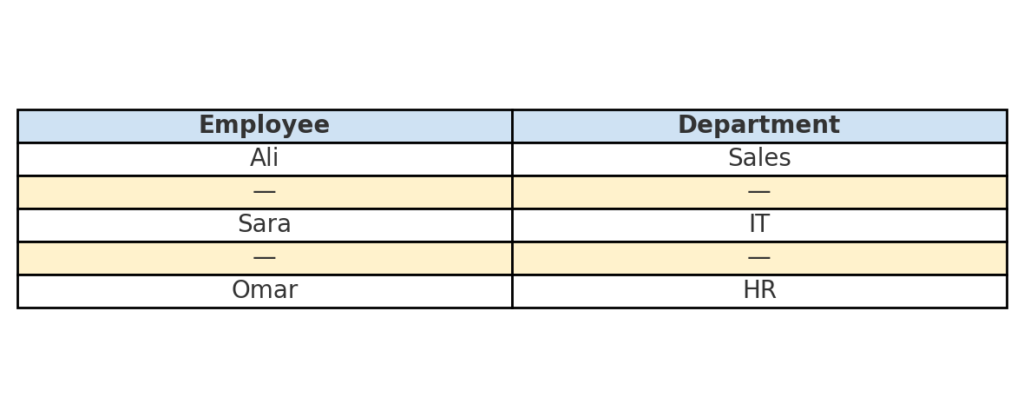
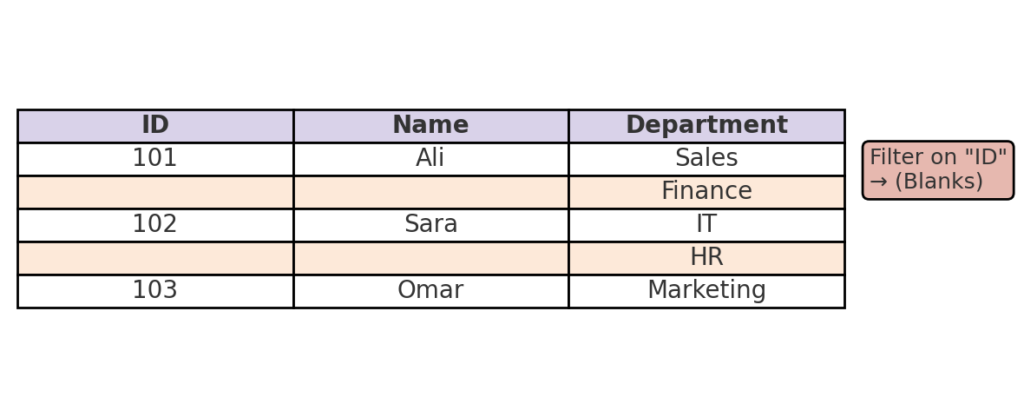
Method 2: Use Filters to Identify and Delete Empty Rows
This method works best when some rows have incomplete data. You can delete only the rows with an empty key column.
Steps:
- Select your dataset and click Data > Filter.
- Apply a filter to a column you expect to always have data (like ID or Name).
- Filter that column to show only (Blanks).
- Select the visible rows, right-click, and choose Delete Row.
- Remove the filter to return to the full dataset.
This method is safer for partial rows. It helps you avoid deleting rows that have valid data in other columns.
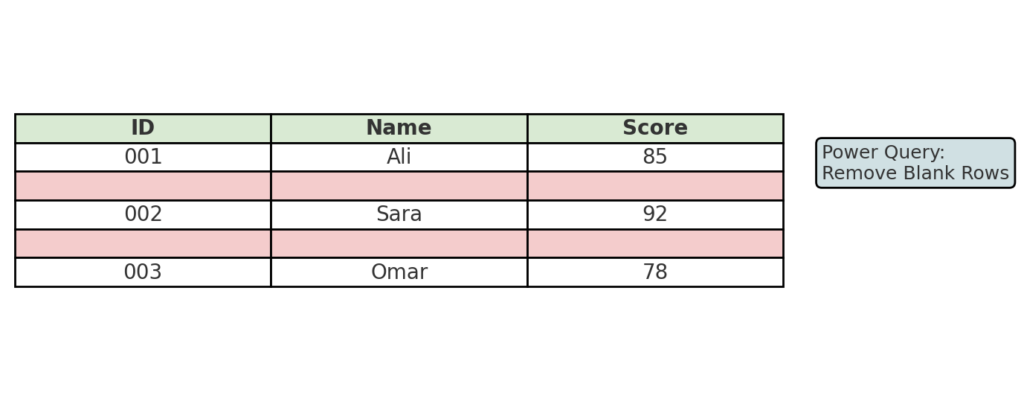
Method 3: Use Power Query to Remove Empty Rows (Best for Repeated Cleaning)
If you often clean similar datasets, use Power Query. It’s efficient and easy to repeat.
Steps:
- Select your data range and go to Data > Get & Transform > From Table/Range.
- In the Power Query Editor, select Remove Rows > Remove Blank Rows.
- Click Close & Load to bring the cleaned data back into Excel.
Power Query refreshes as your source data changes. This makes it great for ongoing projects and automation.
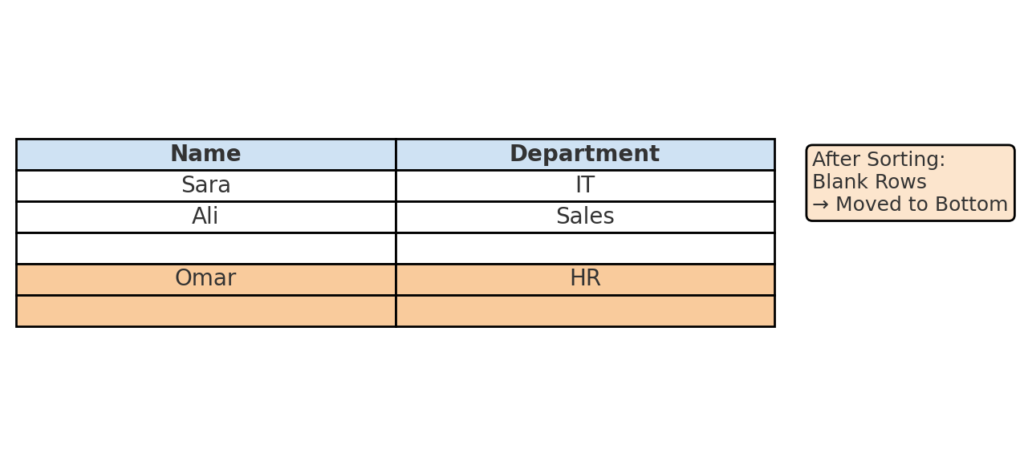
Method 4: Use Sorting
Sorting your data can sometimes push empty rows to the bottom. This makes it easier to delete them all at once.
Steps:
- Select the dataset.
- Go to Data > Sort.
- Sort by any column in ascending or descending order.
- Scroll down, select the empty rows, right-click, and choose Delete.
This is especially helpful when your dataset includes rows with partial blanks.
Examples
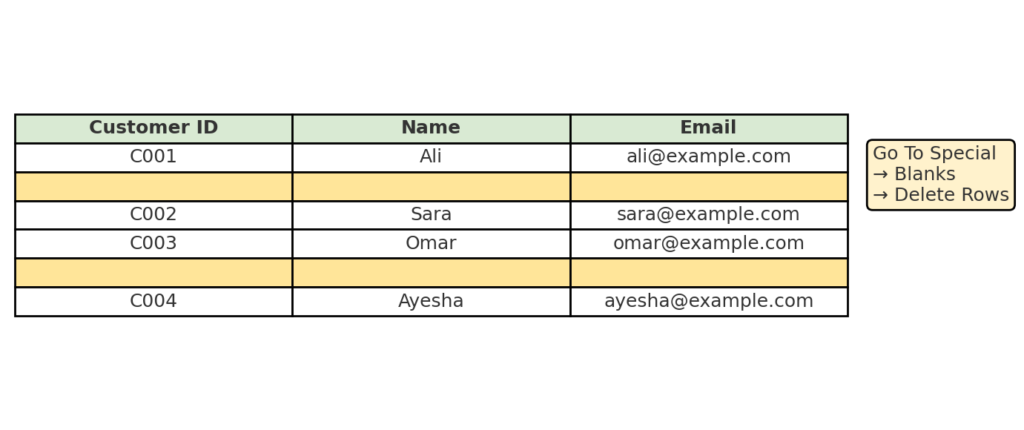
Example 1: Cleaning Exported CRM Data
You export customer data from a CRM system, and every few entries include an empty row. Using Go To Special, you delete these rows to prepare the data for import into another system.
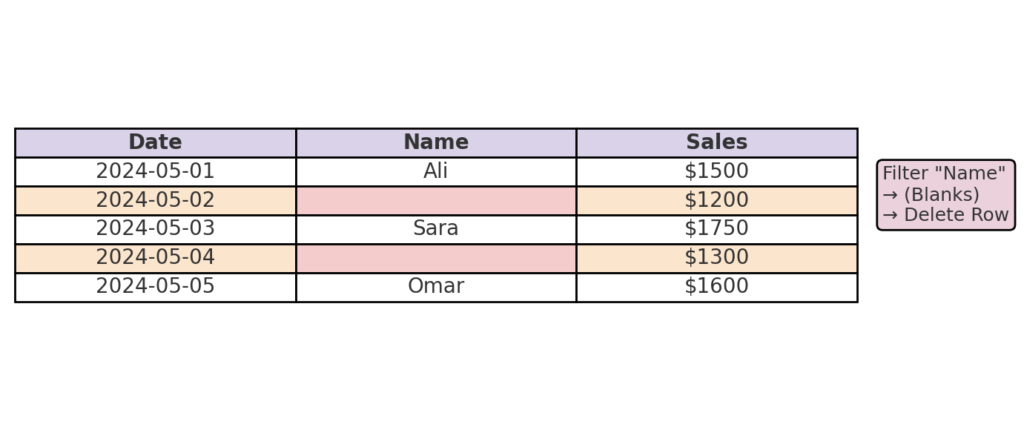
Example 2: Sales Tracker With Gaps
Your sales data has manual entries from several weeks. However, some users left blank rows between these entries. Use “Filter by blank names” to remove rows safely. This won’t affect data with values in other fields.
Benefits of Deleting Empty Rows in Excel
Improves Data Accuracy and Analysis
Blank rows can mess up Excel formulas. This is true for functions like SUM, AVERAGE, and LOOKUP that need continuous ranges. Removing them ensures accurate calculations and prevents skewed results.
Enhances Spreadsheet Performance
Large workbooks with many empty rows can slow processing, increase file size, and waste memory. Cleaning up improves performance and responsiveness.
Simplifies Data Navigation and Visualization
Empty rows make it harder to scroll, filter, or graph your data. Taking them away gives you a clearer view. It also makes charting, sorting, and filtering easier.
Prevents Errors in Formulas and Macros
Many formulas assume continuous data. Blank rows break these patterns, leading to incorrect results or macro failures. Deleting them ensures your Excel logic works as intended.
Facilitates Easier Data Imports
Third-party systems (such as databases or CRMs) may reject spreadsheets with structural issues. Clean rows ensure your data can be imported without errors or reformatting.
How to Delete Blank Rows in Excel
FAQ’s
Why are there so many empty rows in my Excel file?
Empty rows can show up when you import data, copy-paste from websites, or delete content manually without removing the row.
How do I delete all blank rows quickly?
Use Go To Special > Blanks, then delete the selected rows using Delete Sheet Rows. For automation, consider using Power Query or a VBA macro.
Will deleting blank rows affect my formulas?
If your formulas reference specific row numbers, deleting rows may change those references. Use structured tables or dynamic ranges (like OFFSET or INDEX) to avoid issues.
Conclusion
Learning how to delete empty rows in Excel is a fundamental part of cleaning and preparing your data. Removing blank rows makes your data tidy and accurate. This is true for small spreadsheets and large imported files. It also makes your data easier to work with. Excel offers many ways to make your work easier. You can use built-in tools like Go To Special and filters. You can also try more powerful methods like Power Query and VBA. Clean spreadsheets improve analysis, boost performance, prevent errors, and look professional
