Merging date and time values in Excel makes working with timestamps, logs, time entries, and schedules easier. This approach helps with calculations, sorting, and data analysis. Excel keeps dates and times as numbers. So, combining them correctly is important for accuracy and consistency. In this article, you’ll discover what date and time mean in Excel. You’ll learn how to combine them with simple formulas. We’ll explore practical examples, answer common questions, and give you expert-level knowledge.
What is Date and Time in Excel?
In Excel, dates and times are numeric values that represent specific points in time.
- Dates are stored as whole numbers, where 1 represents January 1, 1900.
- Times are stored as decimal fractions of a day. For example, 0.5 equals 12:00 PM (halfway through the day).
Example:
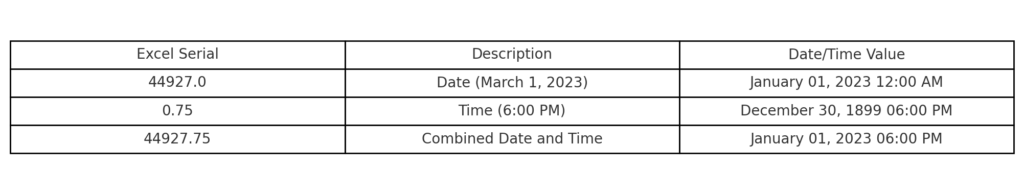
- 44927 = Date (March 1, 2023)
- 0.75 = Time (6:00 PM)
- 44927.75 = Combined Date and Time (March 1, 2023, 6:00 PM)
Understanding this structure allows you to manipulate and combine date and time easily using Excel formulas.
How to Combine Date and Time in Excel?
There are multiple methods to combine date and time values in Excel depending on your dataset. Below are the most reliable ones.
Method 1: Using Addition (+ Operator)
If Column A has the date and Column B has the time:
=A2 + B2
This adds the numeric values behind the date and time, resulting in a full datetime value.
Optional: Format the Result
- Right-click the result → Format Cells
- Choose Custom → Use format:
m/d/yyyy h:mm AM/PM

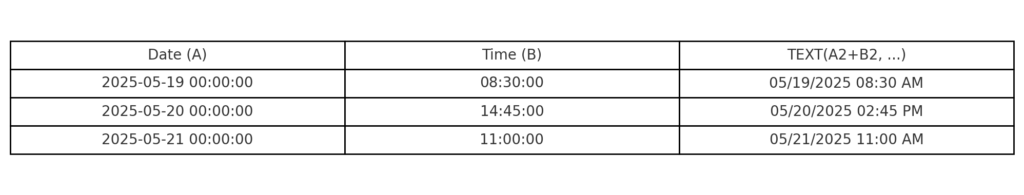
Method 2: Using the TEXT Function
To display date and time in a custom readable format:
=TEXT(A2 + B2, “mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm AM/PM”)
This keeps the value as text, ideal for reports or exporting.
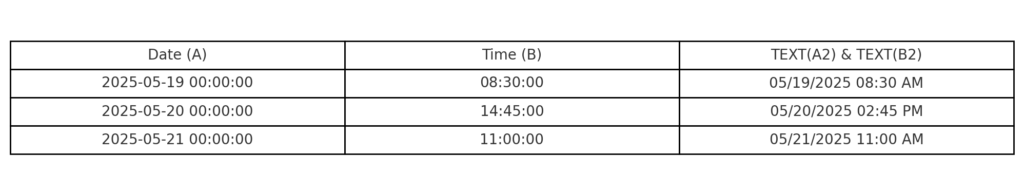
Method 3: Use CONCATENATE or TEXTJOIN (For Text Format)
If you want the result as a string:
=TEXT(A2,”mm/dd/yyyy”) & ” ” & TEXT(B2,”hh:mm AM/PM”)
This keeps the format readable but not usable for calculations. It’s best for labels or display purposes.
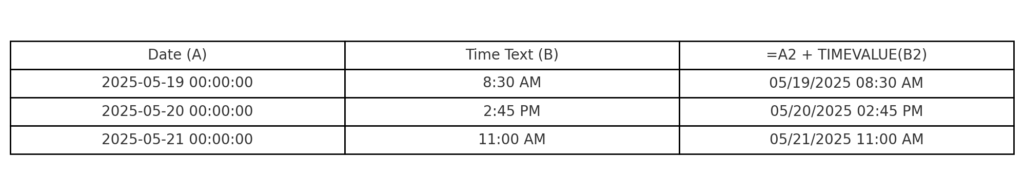
Method 4: Date + Time Using TIMEVALUE
If the time is in text format (e.g., “2:30 PM”):
=A2 + TIMEVALUE(B2)
This converts the time string into a numeric time before combining.
Examples of Combining Date and Time in Excel
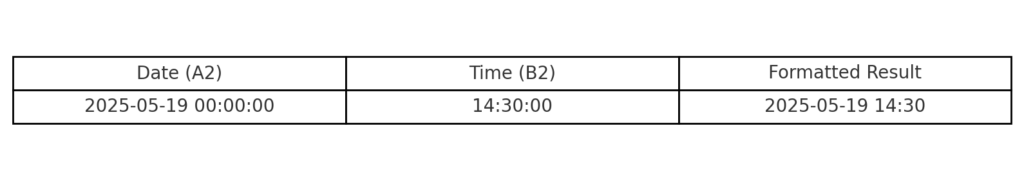
Example 1: Timestamp Creation
Suppose:
- Cell A2 contains a date: 2025-05-19
- Cell B2 contains a time: 14:30 (2:30 PM)
Formula:
=A2 + B2
Result:
2025-05-19 14:30
Tip: Format the cell as Custom → yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm to see both date and time.
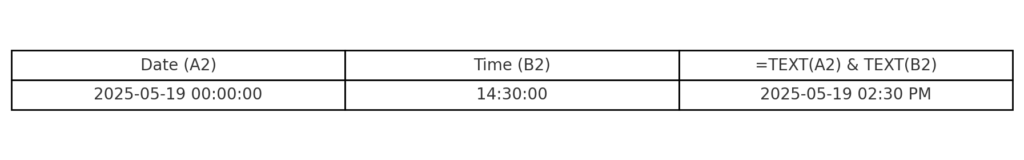
Example 2: Date in Text, Time in Text
=TEXT(A2,”yyyy-mm-dd”) & ” ” & TEXT(B2,”hh:mm AM/PM”)
Result:
2025-05-19 02:30 PM
Example 3: Log Event Tracking
- Use a single column to store complete timestamps for events like user login/logout.
- Formula: =DateCell + TimeCell and apply custom datetime format.
How to combine date and time columns in Excel
FAQ’s About Combining Date and Time in Excel
Why is Excel showing a strange number after combining date and time?
That number is the serial value behind the datetime. Apply formatting (Ctrl + 1) to display it correctly as a date and time.
Can I subtract two combined date-time values?
Yes. Subtracting two datetime values gives the difference in days (with decimals). Multiply by 24 to get hours:
=(EndDateTime – StartDateTime) * 24
What format should I use to display both date and time?
Use custom format:
m/d/yyyy h:mm:ss AM/PM
This ensures clarity and compatibility for both human readers and systems.
What if the time column is in text format?
Use TIMEVALUE() to convert it:
=A2 + TIMEVALUE(B2)
Will this work in Excel Online or Google Sheets?
Yes. All these formulas are compatible with Excel desktop, Excel 365, and Google Sheets—with only minor format differences.
Conclusion
Joining date and time in Excel is an essential skill. It helps with data tracking, time-stamping, scheduling, and more. Merging values helps you manage attendance logs, timestamp transactions, and prepare dashboards. This skill gives you better control over your data.
