
Microsoft Excel is a powerhouse tool for data analysis, reporting, and automation. Many users know about formulas, charts, and tables. But sheet grouping is a feature that often gets overlooked. This feature lets you work on multiple worksheets at the same time. It can boost your productivity significantly. In this guide, we’ll cover grouping sheets. We’ll explain what it means and how to do it step-by-step. You’ll see real-world examples and learn about its benefits. We’ll also answer common questions
What is Grouping Sheets in Excel?
Grouping sheets in Excel lets you select several worksheets. This way, any action you take—like formatting cells, entering data, or inserting formulas—applies to all the selected sheets at once.
Key Features of Grouped Sheets:
- Simultaneous editing across multiple sheets
- Universal formatting
- Uniform formula application
- Efficient printing and page setup
When sheets are grouped, they act as mirrors. For instance, if you type a value in cell A1 on one sheet, it appears in the same cell on all grouped sheets.
Real-World Use Cases:
- Monthly reports that have the same structure (Jan, Feb, Mar…)
- Departmental sheets (Sales, Marketing, HR) requiring the same formatting
- Invoices or templates shared across multiple clients
How to Group Sheets in Excel (Step-by-Step Instructions)
Grouping sheets is a straightforward process. Here’s how to do it:
Method 1: Grouping Adjacent Sheets
- Open your Excel workbook.
- Hold the Shift key on your keyboard.
- Click the first sheet tab.
- Then click the last sheet tab you want to group.
All sheets between the two selected will be grouped.

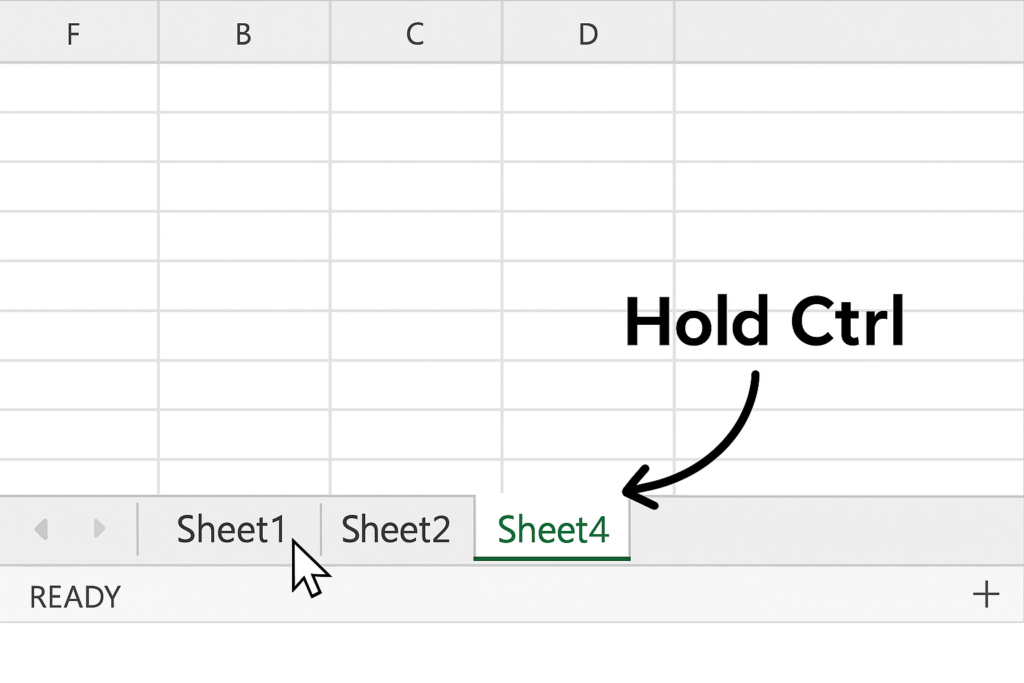
Method 2: Grouping Non-Adjacent Sheets
- Hold the Ctrl key.
- Click each sheet tab you want to group individually.
This lets you select sheets that are not next to each other.
How to Know Sheets Are Grouped?
You’ll see the word [Group] next to the workbook name in the title bar.
How to Ungroup Sheets
- Right-click any of the grouped tabs and click Ungroup Sheets, OR
- Click on any single sheet tab outside the group.
Examples of Grouping Sheets in Excel
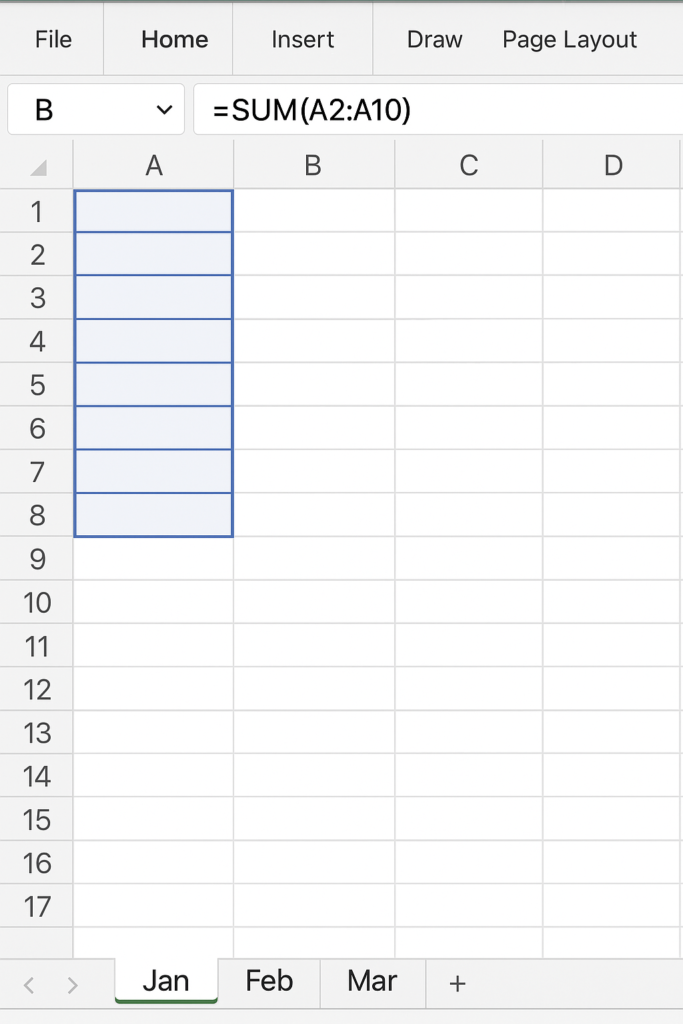
Example 1: Entering Data Across Multiple Months
Suppose you have sheets named Jan, Feb, and Mar. You want to enter the same revenue formula in cell B2 of each sheet:
- Group the sheets (Jan to Mar).
- Enter =SUM(A2:A10) in cell B2.
- Press Enter.
The formula will appear in cell B2 on Jan, Feb, and Mar sheets simultaneously.
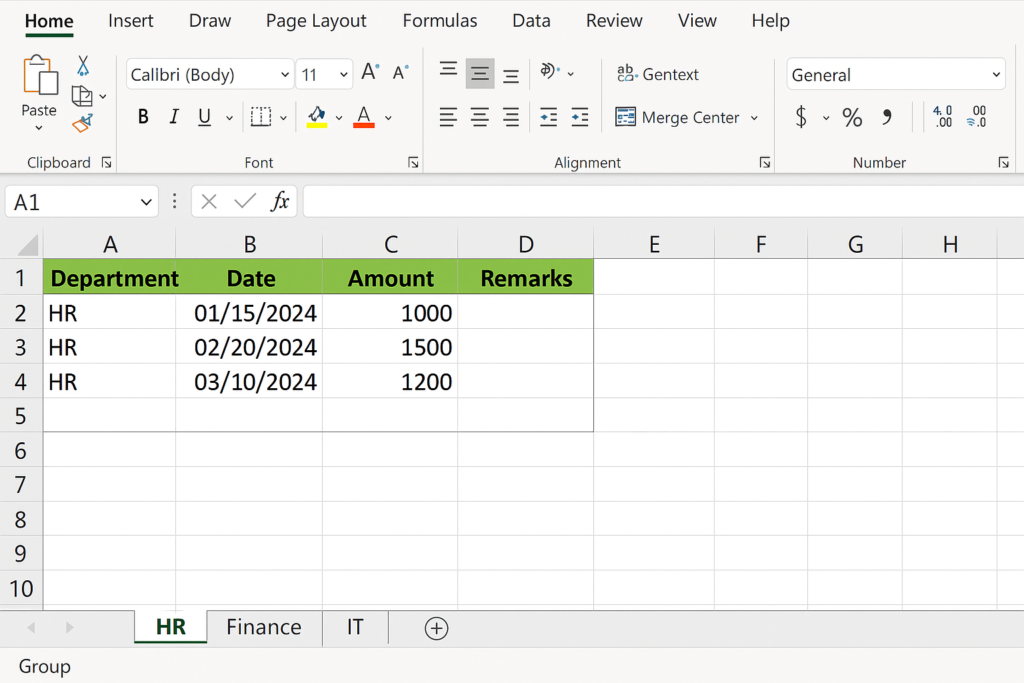
Example 2: Formatting Reports Consistently
You need all departmental sheets to have the same header color and font style:
- Group all department sheets.
- Format Row 1 with bold font and background color.
- Ungroup the sheets.
Now all grouped sheets carry the same formatting, saving time and effort.
Example 3: Print Settings Across Sheets
Group all sheets to adjust print margins or orientation at once.
- Set Landscape orientation
- Adjust margins
- Add headers and footers
All sheets will inherit the print settings instantly.
Benefits of Grouping Sheets in Excel
Time-Saving Automation
Grouping allows batch edits, reducing repetitive actions. For example, if 12 sheets stand for each month, using a grouped format saves you from doing the same task 12 times.
Consistency Across Data Sets
Grouping keeps headers, formulas, and formatting the same across all worksheets. This is useful when every worksheet needs to follow the same structure. This ensures that analysis across sheets is accurate and standardized.
Centralized Input
Grouped sheets allow you to manage data inputs centrally. You can update all sheets with one change. Perfect for template-based designs like payroll slips or inventory logs.
Streamlined Printing and Exporting
You can set print areas, change orientation, and adjust margins for multiple sheets all at once. This is incredibly useful when printing multiple forms or reports.
Reduces Human Error
Grouping automates changes, so you don’t have to edit each sheet by hand. This cuts down the risk of missing updates or making them inconsistently.
Perfect for Template Creation
Developers and Excel experts often group sheets to create consistent templates. Once ungrouped, each sheet retains the structure for individualized data entry.
Improved Collaboration and Scaling
In shared files, grouped editing ensures that multiple team members can work on consistent sheet structures without confusion. Grouping also helps scale documents effectively for larger datasets.
FAQ’s About Grouping Sheets in Excel
Will grouping overwrite existing data?
No. Grouping only mirrors new actions across sheets. Existing values will not be changed unless you overwrite them manually.
Can I use grouping in Excel Online or Excel for Mac?
Yes, you can group in Excel on Windows, Mac, and Office 365 Online. The UI options might look a bit different, though.
Is it possible to apply formulas to grouped sheets?
Absolutely. Any formula entered on one grouped sheet will reflect on all others in the exact same cell location.
How do I avoid accidental grouping?
Before editing, check the title bar. If you see [Group], ungroup it first. This prevents unintentional changes to multiple sheets.
Can I copy or move grouped sheets?
No. Copying or moving works only on individual sheets. You must ungroup them first to move them individually.
Can I protect grouped sheets simultaneously?
Protection needs to be applied individually. Grouping does not allow simultaneous sheet protection via the “Protect Sheet” option.
Conclusion
Grouping sheets in Excel helps you manage, format, and update multiple worksheets at once. No matter if you’re an analyst, accountant, educator, or small business owner, this feature saves time. It also reduces errors and keeps your data consistent across your workbook. Mastering sheet grouping improves your Excel workflow. It also meets today’s productivity standards.
