
If you’re working with data in Microsoft Excel, organization is key. You may need to switch two columns of data. This could be to make it easier to read, follow formatting rules, or fit a new data structure. That’s where knowing how to swap columns in Excel becomes incredibly useful. Swapping columns is quick and easy. It saves time and boosts your workflow. This is especially helpful with large datasets or dynamic reports. Moving data between columns in Excel is key. It helps you manage product catalogs, employee databases, or client contact lists. You need to know how to do this without losing content or breaking formulas.
What is Swap?
In Excel, swap refers to the process of interchanging the position of two columns or data sets. Swapping is different from just moving a column. It means you take the contents of one column and switch them with another. So, both columns trade places. This action does not just shift columns over; it replaces the positions of both.
Swapping is especially useful when:
- Data columns are in the wrong order
- You want to reorganize data for printing or analysis
- You’re preparing spreadsheets for import into another system
- You want to match a template structure
Excel doesn’t have a single “Swap Columns” button, but there are several reliable ways to accomplish this manually or with shortcuts.
How to Swap Columns in Excel
Swapping columns in Excel can be done using drag and drop, cut and paste, or helper columns. Each method is suitable for different situations. Here’s a complete breakdown:
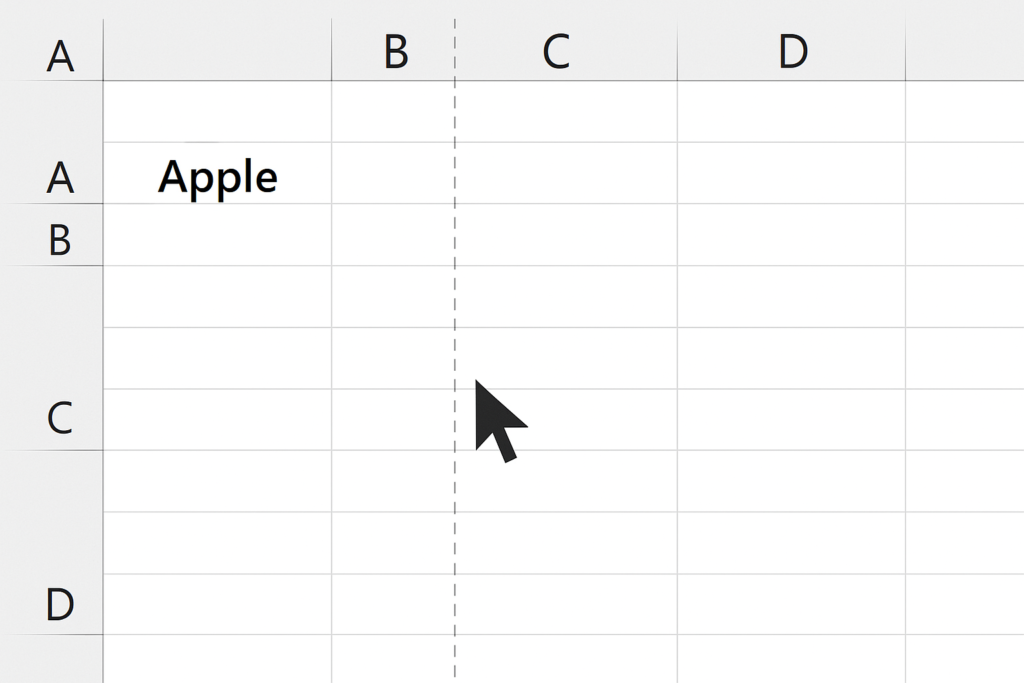
Drag and Drop with Shift Key (Fastest Method)
This method is the easiest and most visual, especially in a simple spreadsheet.
Steps:
- Select the entire column you want to move by clicking the column header (e.g., Column A).
- Hover over the border of the selected column until the cursor turns into a move icon (cross with arrows).
- Hold down the Shift key.
- Drag the column to the new location where you want to place it.
- Release the mouse when you see a vertical line at the new position.
To swap two columns, repeat the process for the second column.
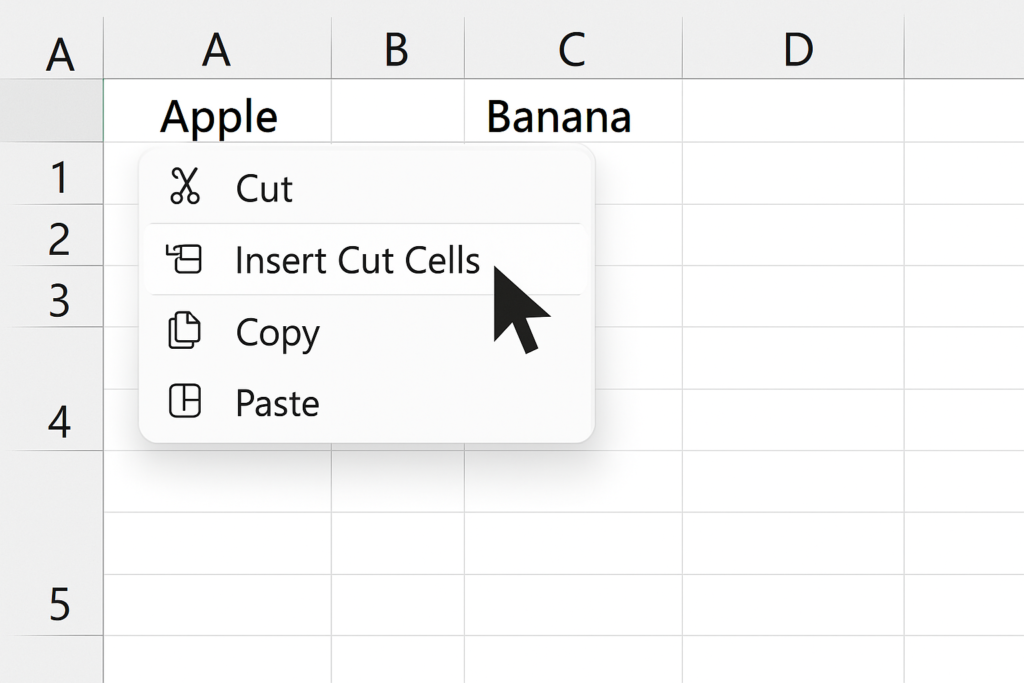
Cut and Insert Method (Safe for Large Datasets)
If you’re dealing with multiple columns and want more precision:
Steps:
- Select the first column (e.g., Column B).
- Right-click and choose Cut.
- Right-click on the column where you want to insert it (e.g., Column A).
- Choose Insert Cut Cells.
Now repeat the same steps for the second column. This method avoids accidental overwriting and works best when exact control is needed.
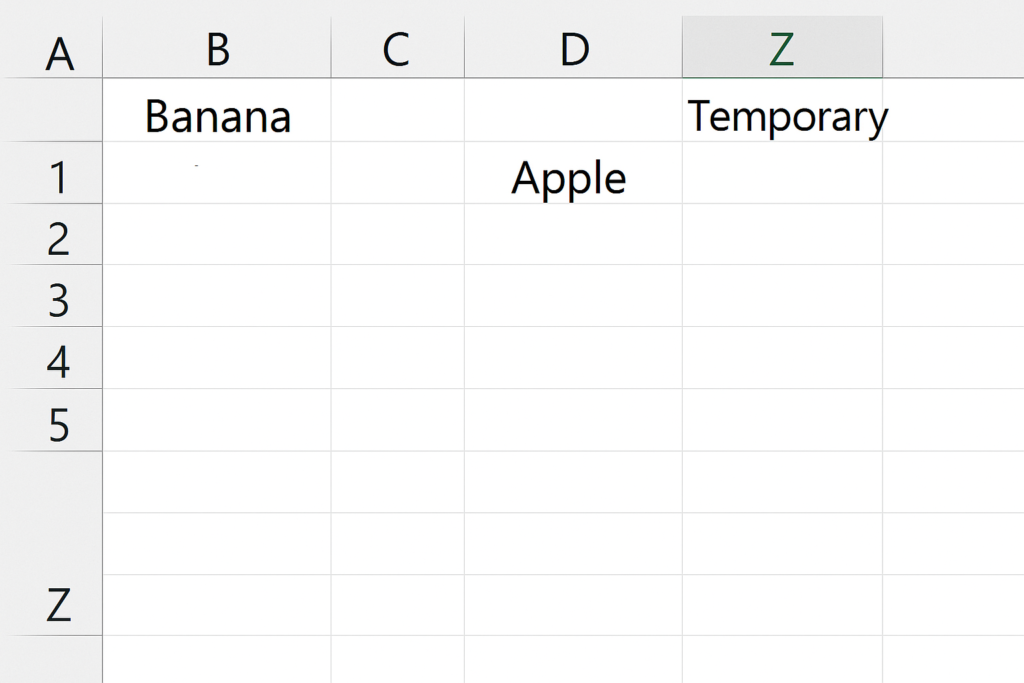
Using a Helper Column (Safe but Manual)
If you’re unsure and want a backup, use a helper column to temporarily hold one column’s data.
Steps:
- Copy Column A and paste it into a temporary column (e.g., Column Z).
- Copy Column B and paste it into Column A.
- Copy the helper column (Z) and paste it into Column B.
- Delete the helper column after confirming the swap.
This is a bit longer but guarantees no data loss and is ideal for beginners.
Examples of Swapping Columns in Excel
Example 1: Reordering Columns in a Customer Database
Your customer list has “Email” in Column C and “Phone Number” in Column D. To match the CRM import template, move the phone number to come before the email. Using the drag and drop with Shift method, you quickly switch Columns C and D to match the required format.
Example 2: Preparing a Product List for Marketplace Upload
Your Excel sheet has product titles in Column A and SKU codes in Column B. The third-party platform needs the SKUs to be listed first. Use the Cut and Insert method to switch the two columns fast. This way, your formulas and formatting stay the same.
Benefits of Swapping Columns in Excel
Saves Time in Reorganizing Data
Swapping columns is much faster than manually copying and pasting every cell. Especially in large datasets, efficient swapping helps you rearrange your spreadsheet in seconds. This is key during reporting deadlines, presentations, or when getting ready to upload to business systems. Fast data organization translates directly to improved productivity.
Improves Data Readability
Often, the order of data matters—especially in reports, dashboards, or customer-facing documents. Swapping lets you reorganize columns to match logical flow, such as placing “Name” before “Date of Birth,” or “Revenue” before “Cost.” Well-structured spreadsheets reduce errors and improve interpretation.
Enhances Compatibility with External Systems
Many applications and tools require Excel imports to follow a specific column order. Swapping columns ensures that your sheet meets import or API requirements. This is particularly helpful in HR, CRM, e-commerce, and finance platforms. Avoiding format mismatches prevents failed imports and saves troubleshooting time.
Reduces Human Error
Using reliable swap techniques can help you avoid deleting or overwriting cells. Using helper columns or VBA makes every step easy to trace and undo. Safe data manipulation is crucial in sensitive environments like accounting or auditing.
3 Ways to Swap Columns in Excel
FAQ’s
How do I swap non-adjacent columns?
Use the cut and insert method for each column separately. First, cut Column X and insert it next to Column Y, then repeat the process in reverse. This maintains structure without overwriting.
Can I undo a column swap?
Yes. Press Ctrl + Z immediately after swapping to undo the action. Excel maintains a history of your actions during the session.
Will formulas break after swapping columns?
No, as long as you don’t overwrite or delete referenced columns. Excel updates relative cell references automatically. Double-check formulas that use absolute references, like $A$1. These references don’t change positions.
Conclusion
Swapping columns in Excel may seem minor, but it is key for data management, reporting, and system integration. Switching two columns safely and efficiently can save time. It also improves accuracy and makes your spreadsheet easier to use. This is especially helpful in busy business settings. You can choose quick drag-and-drop tools or advanced automation with VBA. Each method has its use based on how complex your dataset is.
